Programmable Controllers
Programmable Logic Controllers, along with easy-to-use Support Software, are available to flexibly handle applications from small-scale equipment to entire production lines with Programmable Logic Controllers such as those in the SYSMAC CJ1, CS1 and other series.
|
|
Features |
| Principles | Classifications |
| Engineering Data | Further Information |
|
|
Troubleshooting |
-
 Installation of FA Control Panel
Installation of FA Control Panel
-
 Connecting a Computer Running Support Software (e.g., CX-Programmer) to a FA Controller
Connecting a Computer Running Support Software (e.g., CX-Programmer) to a FA Controller
Installation of FA Control Panel
Introduction
In order to ensure the reliability and security of the system, prior to the design of the system it is important to make certain that the conditions in which it will be installed is well understood.
Basically, the stresses on the FA Controller system (temperature, humidity, vibrations, shocks, corrosive gases, overcurrent, noise etc.) need to be reduced as much as possible. However, the extent to which measures need to be taken in this regard will depend upon the likelihood of problems arising, the conditions in which the system is installed, and the cost of implementing measures. By taking advanced measures to prevent problems, the reliability of the system can be improved, and in the long-term the operation rate can also be increased.
For the individual specifications of each unit, please see the respective user manuals.
Installation/Conditions of Control Panel
The following describes the environmental conditions and measures to be taken for the installation of the control panel (hereafter, "the panel")
Temperature
Based on the operating temperature of the element parts of the FA Controller, the operating temperature for the system is generally between 5°C and 40°C. At the same time, with both forced and natural cooling of the panel, the fact that it is miniaturized to save space means that from our experience the temperature of the panel is sometimes 10°C to 15°C higher than the ambient temperature of the room. As such, it is important that the following measures be taken depending on the installation site and the temperatures being generated to make certain that the panel's internal temperature does not exceed the range of the unit operating temperature, and to provide a sufficient margin for the range of operating temperature.
High Temperature (see Figure 1)
(1)Natural Cooling (Natural draft at the top and bottom of Panel)
When installing the panel, it is optimal not to make use of cooling devices such as fans and coolers. The following are important points in the installation of the Controller.
Do not install in the upper part where the warm air in the panel stagnates
In order to ensure ventilation space, maintain a sufficient distance from other machinery, wiring ducts etc around the panel
Do not install in positions other than those specified (for example upside down), which can lead to the generation of abnormal heat within the Controller
Do not install directly above devices that generate heat such as heaters, transformers and high-capacity resistors etc.
Avoid direct sunlight
(2)Forced Ventilation (forced ventilation by use of a fan directly mounted at Top of Panel)
(3)Controlled Circulation (controlled circulation by means of a fan in the airtight enclosure panel)
(4)Full Room Cooling
(Use a cooler to cool the entire room in which the panel is installed)
(Notes)
Environmental conditions and cooling system should be as follows.
Panel installed in room with low dust → (1) or (2)
Panel installed in room with dust → (3) or (4)
When using a fan
Attach an air filter to the suction mouth to prevent the entry of dust
Periodically wash the air filter in water.
Temperature sensors should be attached near the Controller to emit an alarm in the event that the fan or air conditioner break down
etc.

Figure 1. Cooling Board
Low Temperature
In cold areas where the morning temperature falls below 0°C at the time of start-up, attach a small space heater inside the panel to heat the internal temperature to about 5°C. In order for the Controller power supply to generate heat, don't turn off the power.
Humidity
In order to maintain the insulating properties of the FA Controller, relative humidity should be kept within the range of 35% to 85%. In particular in the winter, when heaters are turned on and off, sudden changes in temperature may be experienced resulting in condensation which can lead to shorts or malfunctions. Where there is danger of such a change in temperature, power should be kept on during the night and condensation should be prevented through such measures as installing a small heater inside the panel to maintain low heat. (See Figure 2)

Figure 2. Examples of Measures against Condensation
Vibrations/Shocks
The FA Controller is tested in accordance with the environmental (electricity and electrons) the sine wave vibration test method (JIS C0040/IEC68-2-6) and the shock test method (JIS C0041/IEC68-2-27), so that vibrations and shocks in the general specifications will not cause malfunctions. However, the system should not be installed in a place where it will be subject to regular vibrations or shocks, especially to the Controller and the panel.
The following methods may be used to reduce the effect of vibrations and shocks.
(1)For vibrations and shocks that originate externally, the panel should be removed from the source. Alternatively, the Controller and the panel should be protected with the use of rubber.
(2)Isolate vibrations such as through the construction of the building, flooring etc.
(3)Regarding shocks experienced during magnetic contactor operation in the panel, the source of the shock or the Controller should be protected by rubber so that the shock is not felt.
Atmosphere
When using the system in any of the following kind of places, connections may be loosened or elements and parts may experience corrosion, and an air purge should be implemented to avoid this.
(1)Places where dust, salt, particles, soot or organic solvents etc are common, and where the enclosure is sealed in such a way that the internal temperature does not increase very much.
(2)Where corrosive gases are common, an air purge (air purification) of the panel should be performed, to pressurize the panel and prevent the intrusion of air from outside.
(3)Places with flammable gases may be a cause of ignition. The system should not be used without a fire prevention mechanism in place.
Work Space
When installing the FA Controller and the panel, please consider their use, operability and maintenance, and pay particular attention to the following.
(1)Make sure that there is sufficient space to operate programs and to replace the unit. Further, for the sake of saftey and maintenance, installation should be as far as possible from high pressure or high power devices.
(2)Mount the Controller and I/O unit in a position in which the use of the debugging tool and the connection and operation of peripheral devices will be possible.
(3)The Controller and I/O unit generally has a maintenance light, and this should be easy for the operator to see, and in a position where it can easily be reached.
(4)For systems using the Controller as a control system, it is likely that there will be future additions and alterations to the system, so approx. 10- 20% extra space should be allowed for this.
(5)Where necessary, about 600 mm of space should be kept behind the panel for the purpose of performing maintenance.
PLC Control Panel Electrical Conditions
The power supply, grounding, and noise make up the main elements of the electrical conditions. In the installation and wiring of the device, great care must be taken to ensure that there is no danger to the human body, and that electrical signals are not obstructed (noise).
FA Controller Installation Site
For the sake of safety in maintenance and operation, installation should not be near high current (more than 600V) or high power devices. Where this cannot be avoided, installation should be as far away from such devices as possible. (See Figure 3)

Figure 3. Examples of Equipment Arrangement in Panel with High-voltage Device
Arrangement of Controller and Each Unit (See Figure 4)
(1)The CPU and other adjoining units should be special or input units where noise generation is limited.
(2)The coils and contacts in electromagnetic contactors and relays in an external circuit are sources of noise. Locate them at least 100 mm away from the Controller.

Figure 4. Example of built-in type
Power System Wiring (See Diagram 5)
(1)The power supply for the Controller and I/O devices should be separate, and a noise filter should be installed to the Controller power supply.
(2)Noise between the PLC and the ground can be greatly reduced by adding an isolating transformer. In such an event, do not ground the secondary coil of the transformer.
(3)Keep the wiring between the transformer and the Controller as short as possible, twist the wires well, and keep the wiring separate from high-voltage and power lines.
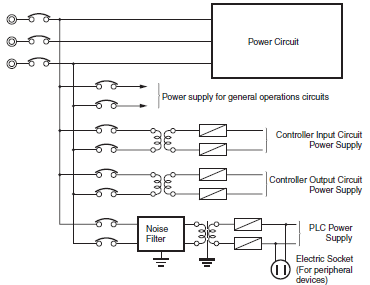
Diagram 5. Power Supply System Diagram
Wiring External I/O Signal Lines
(1)To absorb reverse electromotive force when an inductive load is connected to an output signal, connect a surge protector near the inductive load in an AC circuit, and connect a diode near the inductive load in a DC circuit. (See Diagram 6 and 7)
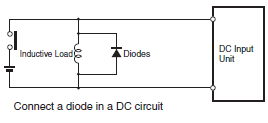
Diagram 6. Input Signal Noise Countermeasures
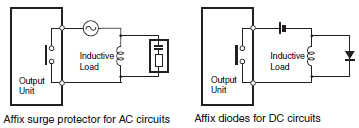
Diagram 7. Output Signal Noise Countermeasures
(2)The output signal line should not be near or parallel with high current or power lines.When nearby, they should be separated by a duct, and an alternative wiring pipe should be established. In this event, the duct and wiring pipe must be grounded. (See Figure 8)
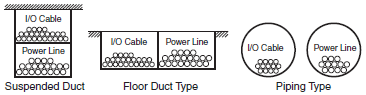
Figure 8. I/O Cable Wiring
(3)Connect the shield to the ground terminal at the Controller, and leave it unconnected at the input device.
(4)Wire the lines so that common impedance does not occur. Such wiring will increase the number of wires, so use common return circuits. Use thick wires with sufficient allowance for the return circuits, and bundle them with lines of the same signal level.
(5)For long I/O lines, wire the input and output signal lines separately.
(6)Use twisted-pair wires for pilot lamps (and particularly lamps with filaments).
(7)Using a CR surge absorber or diode etc is effective in reducing noice sources from input devices or output load devices.
External Wiring
The wiring method can have a large impact on creating a system that is strong against noise and a system that can operate with a high degree of reliability. Wiring, and noise countermeasures in particular, are based on experience, and it is necessary to closely manage wiring based on experience and information in the manuals.
Preventing Faulty Wiring
(1)By attaching marker bands to cables showing their direction, faulty wiring can be prevented, and wiring checks and maintenance can be facilitated.
(2)Use different colors during wiring.
(3)Place wires that transmit the same kind of signal into the same ducts, and separate them into groups.
General Precautions
(1)Do not join wires between terminals.
(2)Support and fix the power line so that its end does not pull at the ends of multi-conductor cable.
(3)Use flexible wires for the movable places such as doors etc. Install them one part on the panel body and the other on the door so that they may not be damaged by the movement of a door.
(4)Connect crimp terminals to the end of the wire and use a torque driver for connection to the terminal, and screw in at an appropriate pressure. For terminal connection to an AC power unit, a roundtype crimp terminal should be used instead of a U shaped terminal, for safety purposes.
(5)The dust protection cover attached to the Controller unit should be kept in place until the wiring is completed to prevent dust from the wiring from entering. Further, as the internal temperature will increase greatly when the unit is in operation, the dust protection cover should be removed once wiring is completed to prevent loss in functionality.
(6)All wiring for the power circuit should be twisted.
(7)The primary or secondary noise filter should not be bundled, as this reduces its effectiveness.
Wiring Route
For the following combination, since signal types, properties, or levels of the signal differs, in principle different cables should be used or different routes should be used. Otherwise, the S/N (signal-to-noise ratio) resulting from electrical induction can fall. Also, by classifying and arranging the wiring, later maintenance or system changes can be simplified.
(1)Power lines and signal lines
(2)Input and output signals
(3)Analog and Digital Signals
(4)High level and low level signals
(5)Communication lines and Power line
(6)DC signals and AC signals
(7)High frequency aparatus (inverters etc.) and signal lines (communication)
Wiring Method
(1)Isolate signal cables with different characteristics when routed in the same duct.
(2)Routing more than one power line in the same duct should be avoided as much as possible. Where this cannot be avoided, place a partition in the duct and ground it. (See Figure 9)
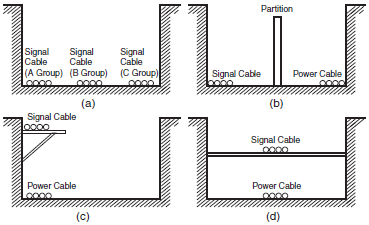
Figure 9. Isolating Signal and Power Cables
(3)When using conduits in the course of wiring, the wires from one circuit should not place wires for a single circuit in separate conduits as the pipes heat up. (See Figure 10)

Figure 10. Parallel use of Electrical Wires (single phase)
(4)Do not install power cables and signal cables in parallel as they will adversely affect each other.
(5)When high-voltage devices are installed in the panel, due to noise, this should be separated as much as possible from high voltage and power lines when wiring. (See Figure 3)
(6)Install the Controller at least 200 mm from any high voltage or power lines, or make sure that the high current and power lines are contained within metal tubing, and ground to a resistance of 100 W. (See Figure 11)
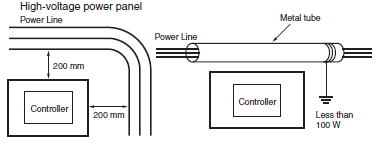
Figure 11. Example of Isolating Controller from Power Line
Other Precautions
(1)I/O modules have plus and minus commons, so be careful of polarity when wiring.
(2)The outside of a fibre optic cable looks similar to a regular communication or power cable, but inside the cable there is the fibre and protective tension members and separators, so care should be taken when using them.
Installation should be performed by the prescribed or standard methods, and care should be taken to not apply excessive shock, bend, twist, or excessive pulling.
The following manuals have been prepared for wiring using fiber optic cables.
(1) SYSMAC C/CV Series Hard Plastic Clad Fiber Manual for laying Fibre Optics Cables (H-PCF) (Manual No. W156-E1)
(2) Controller Link Unit Fibre Optical Ring User Manual (Manual No. W370-E1)
Grounding
Purpose of Grounding
There are two purposes for grounding.
(1)Protective grounding which prevents electrocution to people by maintaining an grounding against leakage, induction and occasional accidents.
(2)Grounding, including that to prevent external noise or noise which emenates from other devices or equipment, or noise that could disturb other devices or equipment, and that is necessary to protect device and system functions.
These grounding issues may need to be resolved through experience and experimentation. It is important to take great care and consideration before performing the grounding.
Grounding Method and Precautions
(1) Principles of One-point Grounding
It would be best to consider that it is grounding that "determines electrical potential". Do not use common return circuits to return currents for grounding. Under normal conditions, do not send current through grounding lines (Do not use common return circuits to return currents for grounding.).
(2) As much as possible use independent ground (keep grounding pole at least 10m away from other grounding poles).
(1)Use Ground to 100 W or less, and use independent ground which is separated from the grounding of other devices (See Figure 12 (a))
(2)If using an independent ground is not possible, then use a common ground as shown in Figure 12 (b). Connect to the ground pole of the other device.
(3)Never connect to the same ground as a device that draws a large amount of power, such as a motor or inverter.
Ground the devices separately to avoid mutually adverse influences.
(4)To prevent electrical shock, do not connect to ground poles (especially steel frames) to which multiple devices are connected.
(5)As much as possible keep the grounding pole close to the Controller, and keep the grounding line short.

Figure 12. Grounding Methods
(3) Grounding Precautions
(1)If the same ground is used for both the signal lines and the enclosure, isolate the channel base (a grounded metal plate inside a control panel) with an insulating material. (See Figure 13)

NJ/NX-series Machine Automation Controllers and CS/CJ-series PLCs have an isolated (floating) mounting structure to make it more difficult to be affected by noise from the installation conditions such as a control panel.
Figure 13. Example: Insulating and Grounding an Enclosure
(2)The panel which contains the Controller must be insulated from other electrical devices. This is to prevent the effect of the leakage of current from other electrical devices.
(3)When there is high frequency equipment nearby, please be sure that the panel which holds the Controller is grounded, in addition to the high frequency equipment.
(4)When grounding the shield conductor in the event of shielded cable used in the wiring of input and output, connect the shield near the Controller to the enclosure ground terminal, as shown in Figure 14. For communication cables, please be sure to maintain shield processing in the communications unit manual.

Figure 14. Shield Cable Grounding
(4) Controller Protective Ground Terminal
The Controller contains the following two ground terminals.

: Protective ground terminal that is always connected to the Controller chassis for the prevention of electric shock.

: Functional ground terminal: Connected to a neutral point in the noise filter to provide a ground when power supply noise causes malfunctioning.
 When properly grounded, the terminals will serve to reduce common mode noise from the power supply, but sometimes the grounding can result in picking up more noise, so care should be taken when using the terminals.
When properly grounded, the terminals will serve to reduce common mode noise from the power supply, but sometimes the grounding can result in picking up more noise, so care should be taken when using the terminals.

Diagram 15. PLC Grounding Terminal
(5) Grounding for AC Power Supply Units When wiring to an AC Power Supply Unit. If one power supply phase of the equipment is grounded, always connect the grounded phase to the L2/N (or L1/N) terminal.

Connecting a Computer Running Support Software (e.g., CX-Programmer) to a FA Controller
This document outlines how to connect a computer running the Sysmac Studio, CX-Programmer, or other Support Software to an FA Controller.
For details, refer to the relevant user’s manual.
Connecting Cables for CJ2

| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | USB A plug connector (female) | CPU Unit | USB B plug connector (female) | USB or Toolbus (USB port) | Commercially available USB cable * (A plug connector (male) - B plug connector (male)) | 5 m maximum | A |
| D-sub, 9-pin (male) | Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 9-pin (female) | Host Link | XW2Z-500S-CV | 5 m | B | ||
| XW2Z-200S-CV | 2 m | ||||||
*A driver must first be installed to make a USB connection.
Connecting Cables for CS1/CJ1
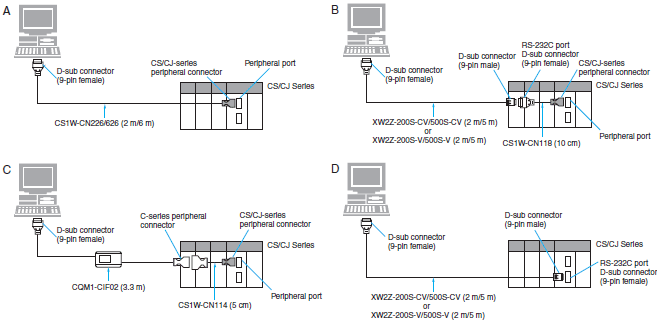
| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | D-sub, 9-pin (male) | CPU | Built-in peripheral port | Peripheral bus or Host Link | CS1W-CN226 | 2 m | A |
| CS1W-CN626 | 6 m | ||||||
| CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-200S-CV | 0.1 m + 2 m | B | |||||
| CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-500S-CV | 0.1 m + 5 m | ||||||
| Host Link | CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-200S-V | 0.1 m + 2 m | |||||
| CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-500S-V | 0.1 m + 5 m | ||||||
| Host Link with a baud rate of 19.2 kbps or less | CS1W-CN114 + CQM1-CIF02 | 0.05 m + 3.3 m | C | ||||
| Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 9-pin (female) | Peripheral bus or Host Link | XW2Z-200S-CV | 2 m | D | |||
| XW2Z-500S-CV | 5 m | ||||||
| Host Link | XW2Z-200S-V | 2 m | |||||
| XW2Z-500S-V | 5 m | ||||||
Reference: USB-Serial Conversion Cable (CS1W-CIF31)
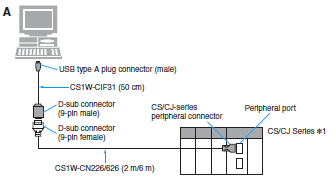
| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | USB A plug connector (female) | --- | RS-232C D-sub, 9-pin (female) | Depends on the Unit's spcifications. | CS1W-CIF31 *2 | 0.5 m | A |
*1Applicable models: CS/CJ Series, C Series (C200HS, C200HE/G/X, C200H, C1000H, C2000H, CQM1, CPM1, CPM1A, CPM2A, CQM1H, and CPM2C), CVM1/CV Series, NS Series, NT Series, SRM1, and ZEN.
*2.A separate cable is required to connect to the PLC.
Connecting Cables for CP1H/CP1L/CP1E
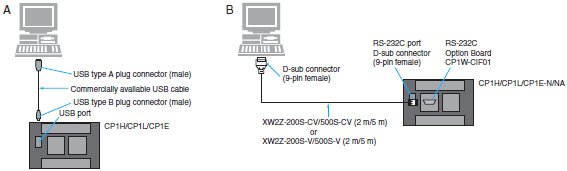
| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | USB A plug connector (female) | CPU | USB B plug connector (female) | USB | Commercially available USB cable (A plug connector (male) - B plug connector (male)) | 5 m maximum | A |
| D-sub, 9-pin (male) | RS-232C port (D-sub 9-pin female) on Option Board * D-sub, 9-pin (female) | Peripheral bus or Host Link | XW2Z-200S-CV | 2 m | B | ||
| XW2Z-500S-CV | 5 m | ||||||
| Host Link | XW2Z-200S-V | 2 m | |||||
| XW2Z-500S-V | 5 m | ||||||
*An Option Board cannot be used with a CP1L CPU Unit with 10 Points and CP1E-E. Also, the CP1E-N and CP1E-NA have a built-in RS-232C port.
Connecting Cables for C200HS/HX/HG/HE

| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | D-sub, 9-pin (male) | CPU | Built-in peripheral port | Peripheral bus *1 or Host Link | CQM1-CIF02 | 3.3 m | A |
| Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 9-pin (female) *2 | Host Link | XW2Z-200S-CV | 2 m | B | |||
| XW2Z-500S-CV | 5 m | ||||||
| XW2Z-200S-V | 2 m | ||||||
| XW2Z-500S-V | 5 m | ||||||
| Host Link Unit C200H-LK201-V1 | Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 25-pin (female) | XW2Z-200P-V *3 | 2 m | C | |||
| XW2Z-500P-V *3 | 5 m | ||||||
*1.These Cables cannot be used for Programming Devices, such as the CX-Programmer, for the C200H-LK201-V1 Host Link Unit on a C200HX/HG/HE-Z PLC.
*2.Only C200HS-CPU21/23/31/33 is equipped with a built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 9-pin (female).
*3.The XW2Z-200S-CV and XW2Z-500S-CV cannot be used.
Connecting Cables for CQM1H
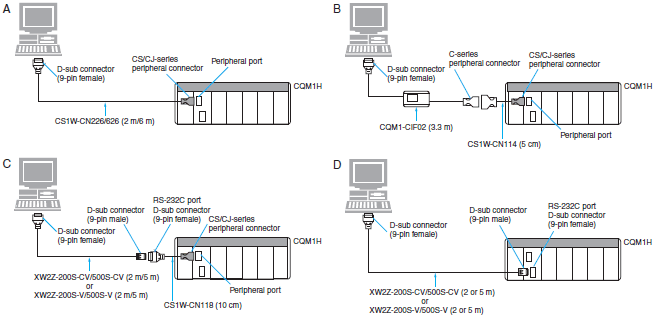
| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | D-sub, 9-pin (male) | CPU * | Built-in peripheral port | Peripheral bus or Host Link | CS1W-CN226 | 2 m | A |
| CS1W-CN626 | 6 m | ||||||
| CS1W-CN114 + CQM1-CIF02 | 0.05 m + 3.3 m | B | |||||
| CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-200S-CV | 0.1 m + 2 m | C | |||||
| CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-500S-CV | 0.1 m + 5 m | ||||||
| CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-200S-V | 0.1 m + 2 m | ||||||
| CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-500S-V | 0.1 m + 5 m | ||||||
| Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 9-pin (female) | Host Link | XW2Z-200S-CV | 2 m | D | |||
| XW2Z-500S-CV | 5 m | ||||||
| XW2Z-200S-V | 2 m | ||||||
| XW2Z-500S-V | 5 m | ||||||
*Discontinuation models in March 2012.
Connecting Cables for CQM1

| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | D-sub, 9-pin (male) | CPU * | Built-in peripheral port | Peripheral bus or Host Link | CQM1-CIF02 | 3.3 m | A |
| Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 9-pin (female) (CPU42/43/44/63/64/65/85 only) | Host Link | XW2Z-200S-CV | 2 m | B | |||
| XW2Z-500S-CV | 5 m | ||||||
| XW2Z-200S-V | 2 m | ||||||
| XW2Z-500S-V | 5 m | ||||||
*Discontinuation models in March 2001.
Connecting Cables for CPM1, CPM1A and CPM2A
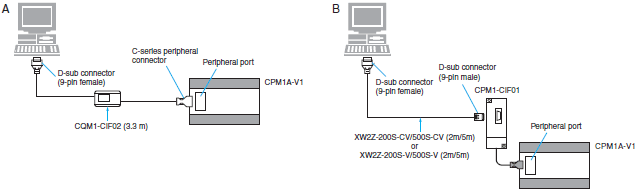
| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | D-sub, 9-pin (male) | CPU Unit | Built-in peripheral port | Peripheral bus * or Host Link | CQM1-CIF02 | 3.3 m | A |
| CPM1-CIF01 + XW2Z-200S-CV | 2 m | B | |||||
| CPM1-CIF01 + XW2Z-500S-CV | 5 m | ||||||
| Host Link | CPM1-CIF01 + XW2Z-200S-V | 2 m | |||||
| CPM1-CIF01 + XW2Z-500S-V | 5 m | ||||||
*CPM2A CPU Units that have a 9 as the fourth digit of the lot number (4 or 5 digits) do not support Toolbus connections. They do support Host Link connections.
Note: Including models whose production are discontinued.
Connecting Cables for SRM1
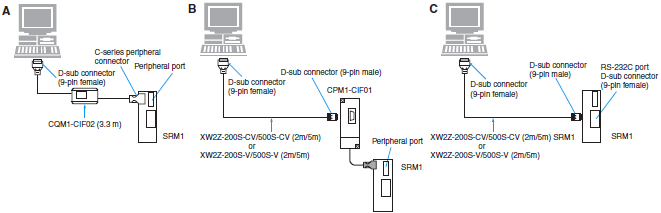
| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | D-sub, 9-pin (male) | CPU Unit | Built-in peripheral port | Peripheral bus or Host Link | CQM1-CIF02 | 3.3 m | A |
| CPM1-CIF01 + XW2Z-200S-CV | 2 m | B | |||||
| CPM1-CIF01 + XW2Z-500S-CV | 5 m | ||||||
| Host Link | CPM1-CIF01 + XW2Z-200S-V | 2 m | |||||
| CPM1-CIF01 + XW2Z-500S-V | 5 m | ||||||
| Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 9-pin (female) (SRM1-C01 only) | XW2Z-200S-CV | 2 m | C | ||||
| XW2Z-500S-CV | 5 m | ||||||
| XW2Z-200S-V | 2 m | ||||||
| XW2Z-500S-V | 5 m | ||||||
Note: Including models whose production are discontinued.
Connecting Cables for CPM2C

| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | D-sub, 9-pin (male) | CPU | Communications port (as a peripheral port) | Peripheral bus *1 or Host Link | CS1W-CN226 *2 | 2 m | A |
| CS1W-CN626 *2 | 6 m | ||||||
| CS1W-CN114 + CQM1-CIF02 | 0.05 m + 3.3 m | B | |||||
| CPM2C-CIF01-V1 + CS1W-CN114 + CQM1-CIF02 | Adapter + 0.05 m + 3.3 m | C | |||||
| CPM2C-CN111 (Peripheral port) + CQM1-CIF02 | 0.1 m + 3.3 m | D | |||||
| Communications port (as an RS-232C port) | Host Link | CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-200S-CV | 0.1 m + 2 m | E | |||
| CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-500S-CV | 0.1 m + 5 m | ||||||
| CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-200S-V | 0.1 m + 2 m | ||||||
| CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-500S-V | 0.1 m + 5 m | ||||||
| CPM2C-CN111 (RS-232C port) + XW2Z-200S-CV | 0.1 m+2 m | F | |||||
| CPM2C-CN111 (RS-232C port) + XW2Z-500S-CV | 0.1 m + 5 m | ||||||
| CPM2C-CN111 (RS-232C port) + XW2Z-200S-V | 0.1 m + 2 m | ||||||
| CPM2C-CN111 (RS-232C port) + XW2Z-200S-V | 0.1 m + 5 m | ||||||
| CPM2C-CIF01-V1 + XW2Z-200S-CV | Adapter + 2 m | G | |||||
| CPM2C-CIF01-V1 + XW2Z-500S-CV | Adapter + 5 m | ||||||
| CPM2C-CIF01-V1 + XW2Z-200S-V | Adapter + 2 m | ||||||
| CPM2C-CIF01-V1 + XW2Z-500S-V | Adapter + 5 m | ||||||
| CPM2C-CIF01-V1 + CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-200S-CV | Adapter + 0.1 m + 2 m | H | |||||
| CPM2C-CIF01-V1 + CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-500S-CV | Adapter + 0.1 m + 5 m | ||||||
| CPM2C-CIF01-V1 + CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-200S-V | Adapter + 0.1 m + 2 m | ||||||
| CPM2C-CIF01-V1 + CS1W-CN118 + XW2Z-500S-V | Adapter + 0.1 m + 5 m | ||||||
| CPM2C-CIF11 + XW2Z-200S-V | Adapter + 2 m | I | |||||
| CPM2C-CIF11 + XW2Z-500S-V | Adapter + 5 m | ||||||
| CPM2C-CIF21 + XW2Z-200S-V | Adapter + 2 m | ||||||
| CPM2C-CIF21 + XW2Z-500S-V | Adapter + 5 m | ||||||
*1.CPM2C CPU Units that have a 9 as the fourth digit of the lot number (4 or 5 digits) and that were manufactured in 1999 do not support Toolbus connections. They do support Host Link connections.
*2.Only Host Link (SYSMAC WAY) connections are possible. Toolbus cannot be used.
Connecting Cables for C1000H, C2000H, C200H
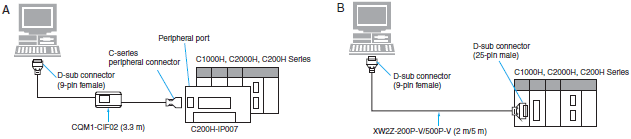
| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | D-sub, 9-pin (male) | CPU Unit | Built-in peripheral port | Host Link | C200H-IP007 + CQM1-CIF02 * | 3.3 m | A |
| Host Link Unit C1000H, C2000H: C500-LK203 C500-LK201-V1 (3G2A5-LK201-V1) C120-LK201-V1 (3G2A6-LK201-EV1) C200H: C200H-LK201-V1 C120-LK201-V1 (3G2A6-LK201-EV1) | Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 25-pin (female) | XW2Z-200P-V | 2 m | B | |||
| XW2Z-500P-V | 5 m | ||||||
*Connection cannot be made from the CQM1-CIF02 directly to a computer for the C200H Handheld Programming Console connecting cable. Use the C200H-IP007.
Connecting Cables for CVM1/CV

| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | D-sub, 9-pin (male) | CPU Unit *1 | Built-in peripheral port | Host Link | CV500-CIF01 *2 | 6 m | A |
| Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 9-pin (female) | XW2Z-200S-V *3 | 2 m | B | ||||
| XW2Z-500S-V *3 | 5 m | ||||||
| Host Link Unit CV500-LK201 *1 (for full duplex communication on port 1) | Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 25-pin (female) | XW2Z-200P-V *3 | 2 m | C | |||
| XW2Z-500P-V *3 | 5 m | ||||||
| Host Link Unit CV500-LK201 *1 (for full duplex communication on port 2) | Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 9-pin (female) | XW2Z-200S-V *3 | 2 m | D | |||
| XW2Z-500S-V *3 | 5 m | ||||||
*1.Discontinuation models in March 2012.
*2.A commercially available 25-pin/9-pin straight conversion cable is separately required.
*3.The XW2Z-200S-CV and XW2Z-500S-CV cannot be used.
Connecting Cables for C500
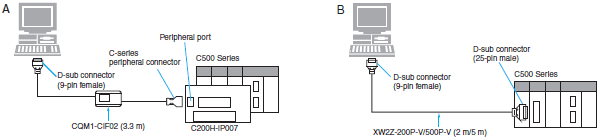
| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | D-sub, 9-pin (male) | CPU Unit *1 | Built-in peripheral port | Host Link | C200H-IP007 + CQM1-CIF02 | 3.3 m | A |
| Host Link Unit *2 C500-LK203 C500-LK201-V1 (3G2A5-LK201-EV1) C120-LK201-V1 (3G2A6-LK201-EV1) | Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 25-pin (female) | XW2Z-200P-V | 2 m | B | |||
| XW2Z-500P-V | 5 m | ||||||
*1.Production of the CPU Units was discontinued in March 2004.
*2.Production of the C500-LK203, C500-LK201-V1 (3G2A5-LK201-EV1), and C120-LK201-V1 (3G2A6-LK201-EV1) was discontinued in March 2006. (There is no recommended substitute product.)
Connecting Cables for C120
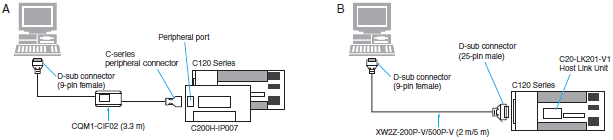
| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | D-sub, 9-pin (male) | CPU Unit *1 | Built-in peripheral port | Host Link | C200H-IP007 + CQM1-CIF02 | 3.3 m | A |
| Host Link Unit *2 C120-LK201-V1 (3G2A6-LK201-EV1) | Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 25-pin (female) | XW2Z-200P-V | 2 m | B | |||
| XW2Z-500P-V | 5 m | ||||||
*1.Production of the CPU Units was discontinued in March 2003.
*2.Production of the C120-LK201-V1 was discontinued in March 2006. (There is no recommended substitute product.)
Connecting Cables for C20P/C28P/C40P/C60P*1, C20K/C28K/C40K/C60K*2

| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | D-sub, 9-pin (male) | Host Link Unit *3 *4 C20-LK201-V1 (3G2C7-LK201-EV1) | Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 25-pin (female) | Host Link | XW2Z-200P-V | 2 m | A |
| XW2Z-500P-V | 5 m | ||||||
*1.Production of the C20P, C28P, C40P, and C60P CPU Units was discontinued in March 2002.
*2.Production of the C20K, C28K, C40K, and C60K CPU Units was discontinued in March 2002.
*3.For connection to C[][]P PLCs, a Host Link Unit is also required in addition to a Connecting Cable.
*4.Production of the C20-LK201-V1 (3G2C7-LK201-EV1) was discontinued in March 2006. (There is no recommended substitute product.)
Connecting Cables for NSJ
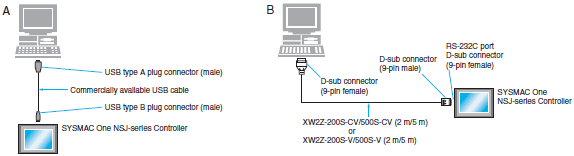
| Computer | Unit | Network Type (Serial Communications Mode) | Model | Cable length | Con- nection Types | ||
| PC port | Unit port | ||||||
| PC/AT compatible | USB A plug connector (male) | CPU | USB B plug connector (female) | USB | Commercially available USB cable (A plug connector (male) - B plug connector (male)) | 5 m maximum | A |
| D-sub, 9-pin (male) | Built-in RS-232C port D-sub, 9-pin (female) | Peripheral bus or Host Link | XW2Z-200S-CV | 2 m | B | ||
| XW2Z-500S-CV | 5 m | ||||||
| Host Link | XW2Z-200S-V | 2 m | |||||
| XW2Z-500S-V | 5 m | ||||||


