RFID Systems
RFID Systems enable non-contact reading and writing of data. Also called electronic tags, IC tags, ubiquitous ID systems, and RF tags, RFID Systems enable non-contact reading and writing of data.
| Introduction |
|
| Principles |
|
| Engineering Data | Further Information |
| Explanation of Terms | Troubleshooting |
What is an ID System?
ID (Identification) usually refers to unique identification of people and objects.
RFID, like barcodes and two-dimensional codes, is used for identifying objects.
Biometrics for uniquely identifying people includes fingerprints, and the iris of the eye.
ID system stands for the Identification System. It is a system to read and identify information on people and things, including AIDC (Automatic Identification & Data Capture).
AIDC uses devices that combine hardware and software and does not require human intervention to identify information obtained from media such as barcodes, 2 dimensional codes, RFID systems, iris, fingerprints, voice etc.

What Is an RFID System?
RFID System is an abbreviation of Radio Frequency Identification System.
It is an "Identification system using wireless communication" that enables transferring data between "RF Tags (or Data Carriers)" that are held by men or attached to objects and "Antenna (or Reader/Writers)". It is a kind of radio communication system.
RFID systems are used in various applications.
Using an RFID system allows consolidated management of objects and information.
Purposes of using RFID in a production site mainly comprises the following applications.
Work instruction (destination instruction)
History management (production history, work history, inspection history, etc.)
Application Example: Work instruction
Can easily build a sorting system that reads the RF tag information of the sorting box using a Reader/Writer installed on the branching point, and uses a control system such as Programmable Controller to switch the point. Automatically performs product sorting based on inspection results.
Prevents mistakes in part identification and thus reduces the losses arising from defects by automatically reading work instructions.
Application Example: History management
Performs work according to the work instructions of the RF tags and writes the results, in the respective processes.
Supports production history management as data on operators, manufacturing dates, and inspection results with time stamp are all contained within the RF tag.
Information such as information inside the RF tag contributes to realization of productivity improvement, quality improvement, traceability, and preventive maintenance.
Features
The main features of RFID are as follows:
1. Able to Read and Write data without direct contact
The RF tag can contain up to several kilobytes of rich information. All of the data required for each process (process history, inspection history etc) can be freely stored, without the need for direct contact. This makes it possible to develop paperless sites, where the causes of production stop are reduced.
2. By "combining an item with its information", a highly pliable and reliable system configuration becomes possible
With the technology to decentralize information, the load on higher systems is reduced. This means that system development costs can also be reduced, systems can be implemented significantly faster, and the system is much more flexible when making changes. Also, "the unification of items with their information" for each process and site can make it possible to manage production/processes and product quality without errors. And, with the latest information contained in RF tags, work can continue offline in emergencies, significantly shortening the time required to restore processes.
3. With the adoption of space transmission technology and protocols, highly reliable communication is made possible
As opposed to barcodes which simply look for 1 or 0, advanced space transmission technologies and specialized protocols are employed for transmission through the air. 16 bits CRC is added to the information as it is transmitted. More than 18 bits Burst errors can be detected at a ratio of 00.9985%, providing a very high reliability in the transfer. Also, since there are no mechanical devices involved such as with the Raster Scan method for barcodes, the likelihood of malfunction and other problems is greatly reduced.
4. Reading and writing is possible without line of sight, using electric and electromagnetic wave transmission
1.Unlike barcodes, since communication occurs by means of electric and electromagnetic waves, erroneous readings due to dirt, moisture, oil etc are cancelled out. Even if there is dust, moisture etc., or anything other than metal between the antenna and the RF tag,. it will not affect transmission. And since the communication range is wide, there is no need for extreme positioning which can greatly reduce the time and cost of design.
5. Can simultaneously access information of multiple RF tags
Some RFID systems are equipped with a function that allows you to simultaneously read the information of multiple RF tags existing within the transmissions area of the Reader/Writer.
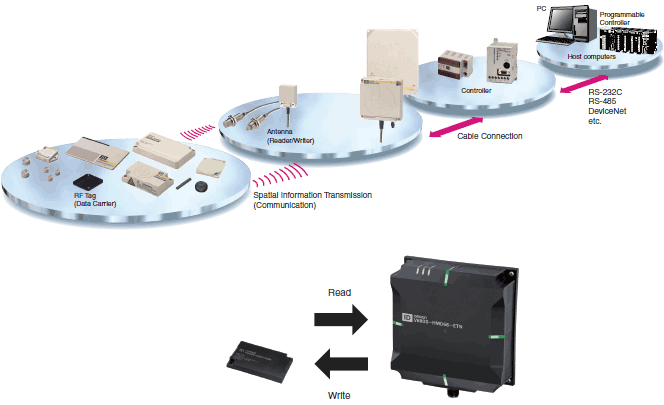
Operating Principles
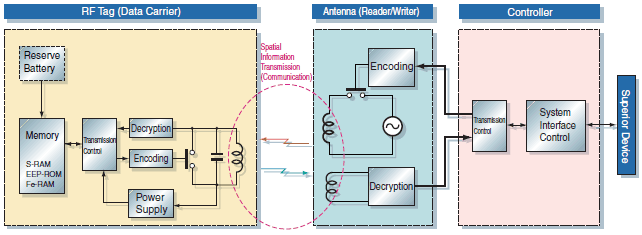
Configuring an RFID system requires RF tags, Reader/Writers, and host devices.
The RFID system writes data sent from the host device to the RF tag via the Reader/Writer.
The data inside the RF tag are read through the Reader/Writer. Data inside the RF tag are rewritable.
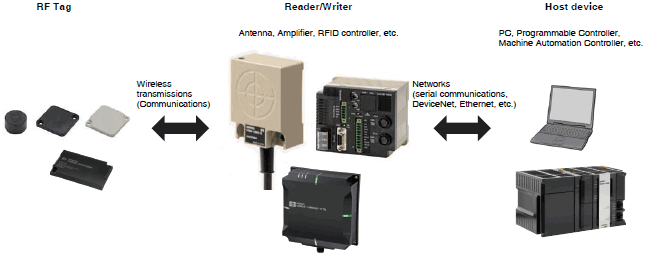
RFID System Function Block Diagram
Classification
Frequency Bands
RFID, which is a system that uses radio waves, is categorized according to its frequency band.
| Frequency | 30 to 300 kHz | 300 kHz to 3MHz | 3 to 30 MHz | 30 to 300 MHz | 300 MHz to 3 GHz |
| Abbreviation | LF Low Frequency | MF Medium Frequency | HF High Frequency | VHF Very High Frequency | UHF Ultra High Frequency |
| Frequency used by RFID | 123/135 KHz | 400 to 530 KHz | 13.56 MHz | Not used by RFID | 433 MHz/ 860 to 960 MHz/ 2.45 GHz |
| Spatial transmission | Electromagnetic induction | Electromagnetic coupling | Electromagnetic induction | - | Microwave |
As a high-frequency radio wave generally has a short wavelength, it can transmit more information within a shorter time.
The radio wave also has the property of traveling in a straight line.
A low-frequency radio wave has the tendency to transmit information stably over a greater distance without being affected by variations in terrain due to its long wavelength.
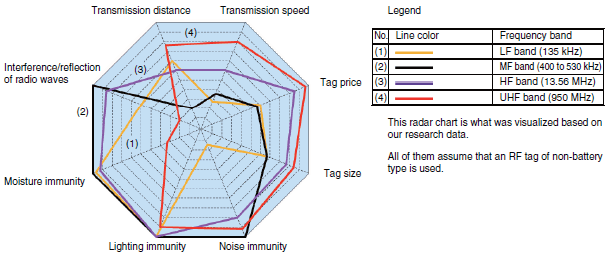
Below is a radar chart of performance comparison by method.
As you can see from the chart UHF has the highest performance for transmission distance, however, regarding to Interference/reflection of radio waves, other bands are superior. HF band has the best performance on average in all areas.
It is necessary to select an RFID system appropriate for the application.
RFID System Transmission Methods
RFID systems primarily use the following three transmission methods.
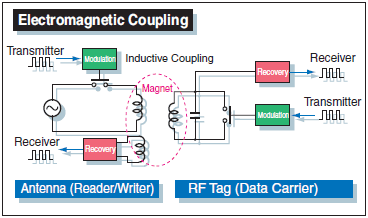
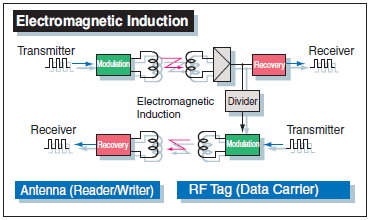
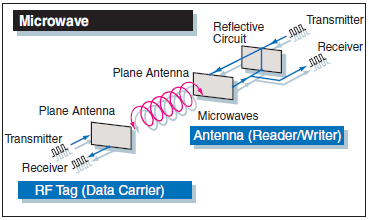
| Transmission method | Electromagnetic coupling | Electromagnetic induction | Microwave (radio wave) | ||
| Communications frequency | 400 to 530 kHz | 120 to 150 kHz | 13.56 MHz | 2.45 GHz | |
| Transmission distance | Not good 0 to 150 mm | Good 0 to 1 m | Not good 0 to 50 mm | Good 0 to 700 mm | Very good 0 to 10 m |
| Data write | Very good | Very good | Very good | Very good | Very good |
| Communications speed (communications rate and processing speed) | Good | Not good | Very good | Good | Very good |
| Communications directivity and sharpness | Not good | Ensure suitability | Good | Not good | Good |
| Influence of reflection/ interference of radio waves | Very good | Not good | Very good | Not good | Ensure suitability |
| Communications stability | Good | Not good | Very good | Good | Good |
| Electromagnetic field noise immunity | Good | Not good | Very good | Good | Very good |
| Optical noise immunity | Very good | Very good | Very good | Very good | Very good |
| Water resistance and oil resistance (influence of moisture) | Very good | Very good | Good | Not good | Ensure suitability |
| Dirt resistance | Very good | Very good | Good | Good | Good |
| Glass and plastic penetration (influence of obstructions) | Very good | Very good | Good | Good | Good |
In a broader sense, electromagnetic coupling is included in the electromagnetic induction.
Besides the frequencies given above, there is also the UHF band (950-MHz band) for radio wave method and other frequencies.
Different communications methods have different features. Understand the advantages and disadvantages of each method before selecting the right communications method for your application.
RF Tags (Data Tags)
A variety of types of RF tags have been manufactured according to their respective applications.
• Classification by Shape
RF tags have various shapes because different applications require different RF tag shapes. Many RF tag types allow you to select the most suitable RF tag shape for your application.

• Classification by Function
OMRON mainly handles RF tags of read/write type.
One feature of RFID is the ability to freely read and write information.
| Item | Read-only type (RO) | Write once read many type (WORM) | Read/write type (R/W) | ||
| Memory types | EP-ROM | EEP-ROM | EEP-ROM | Fe-RAM | S-RAM |
| Function | Not rewritable after write by the manufacturer | Writable once only | Unlimitedly rewritable by user | Unlimitedly rewritable by user | Unlimitedly rewritable by user (with built-in battery) |
| Memory capacity | 10 to 100 bytes | 10 to 100 bytes | 10 bytes to 10 KB | 10 bytes to 10 KB | 1 to 10 KB |
• Classification by Power Supply Method
The most widely used tags are low-price, maintenance-free passive tags.
Active tags are effective for a RTLS (real time locating system) and other location management applications.
| Passive tag | Semi-passive tag | Active tag |
| ・ Operates only with the power supplied from the antenna ・ Transmission distance: 1 mm to 10 m | ・ Operates with both the power supplied from the antenna and the energy from the built-in battery ・ Transmission distance: 1 cm to 10 m | ・ Actively operates with the energy from the built-in battery ・ Transmission distance: 1 to 100 m |


