Counters
|
|
Features |
| Principles |
|
| Engineering Data |
|
| Explanation of Terms | Troubleshooting |
A Counter that performs counting by energizing or deenergizing a built-in electromagnet.
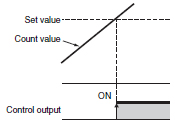
A Counter with a control output that operates when the Counter counts to a set value.
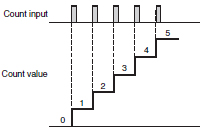
Counter which indicates the total value of the counting inputs and is not provided with a control output.
Addition (Up/Incrementing) Counter
A Counter having an add input and thus capable of counting in an ascending order.
Subtraction (Down/Decrementing) Counter
A Counter with a subtract input and thus capable of counting in descending order.
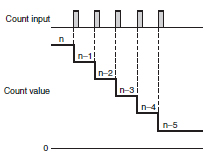
Up/Down Counter
A Counter with the capability of counting in an ascending or descending order, depending on the up-down inputs. Also called a reversible Counter.

The maximum counting speed at which the display and output section of the Counter operates accurately without miscounting.
The maximum counting speed is expressed in units of counts per second (cps).
The ratio of the ON signal time of a given input signal to the OFF signal time of the same input signal. The maximum counting speed of each Counter is determined by counting an input signal with an ON/OFF ratio of 1:1.
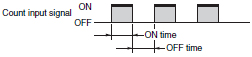
Operating Mode
The control output patterns and display patterns that appear when a Preset Counter counts to the set value.
Examples:
Mode N

Mode C

Note:Refer to the datasheets for individual products for information on operation in other modes.
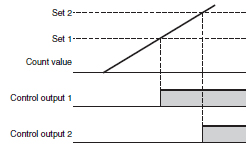
Stage
Number of preset values that correspond with the number of control outputs.
Example: Two-stage Counter
Number of Digits
The maximum number of countable digits.
Display Method
The type of element used to display the counting results.
LED: Light emitting diode
LCD: Liquid crystal display
Note:Electromagnetic Counters display results using a revolving mechanism with printed characters.
Externally Supplied Power
Power that is supplied from the Counter to sensors that are used for counting or resetting. (Also called sensor power.)
To restore the counting, display and output sections of the Counter, to their initial states.
Power Reset
To reset the Counter by turning OFF the power supply voltage.
Auto Reset
To reset the Counter automatically with a signal generated from inside the Counter.
Manual Reset
To mechanically reset the Counter by manual means.
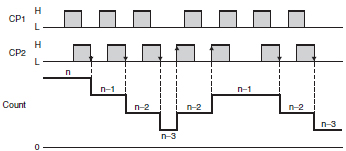
Counting: Operation Method
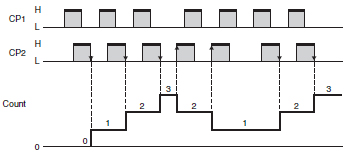
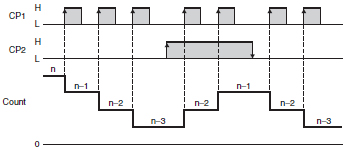
Refer to the following timing charts for the input modes of incremental, decrementing, and up/down (or reversible) Counters. (These charts focus on the up/down input mode.).
Up/Down A Command Input

Up/Down B Command Input
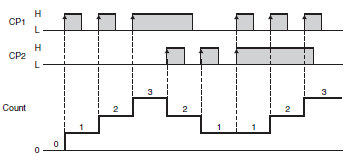
Up/Down C Quadrature Input
Up/Down D Command Input
Up/Down E Individual Input

Up/Down F Quadrature Input