Push Buttons / Indicator Lamps
|
|
Features |
| Principles | Classifications |
| Engineering Data |
|
| Explanation of Terms | Troubleshooting |

| Term | Explanation | |
| Chameleon lighting | Full-screen lighting in one of 3 colors: red, green, or orange. (Orange is produced by simultaneous illumination of red and green.) | |
| Simultaneity | This term is used for switches that have more than one contact circuit. It indicates the difference in time or position between the contacts when all the contacts of the switch are opened or closed in one operation. | |
| LED lighting | LED-lighted models are lit with an LED installed in the base of the Pushbutton Unit. The LED is mounted internally; it cannot be removed. 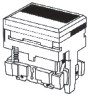 | |
| Incandescent lamp lighting | Incandescent lamp-lighted models are lit with an incandescent lamp. The Lamp (i.e., the incandescent lamp) and the Pushbutton Unit can be separated.  | |
| LED-lamp lighting | LED lamp-lighted models use the same light source as incandescent lamp-lighted models, with an LED instead of a filament. The Lamp (i.e., the LED lamp) and the Pushbutton Unit can be separated. 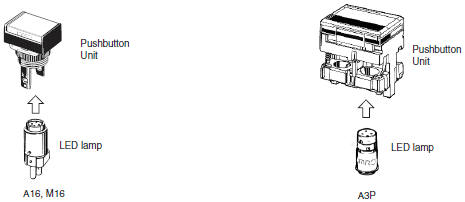 | |
| Voltage Reduction Unit | For 16-dia. A16 (M16) models and 22-dia. A22 (M22) models | The Voltage Reduction Unit has a smoothing circuit and resistor, and lights the 24-VAC/VDC LED lamp by applying 110 (or 220) VAC/VDC directly to the Lamp terminals. |
| Matrix mounting | Mounting several Switches in vertical and/or horizontal lines. | |
| Horizontal side-by-side mounting | Mounting Switches side-by-side with the long side of the Switch (rectangular models) horizontal. | |
| Vertical side-by-side mounting | Mounting Switches side-by-side with the long side of the Switch (rectangular models) vertical. | |
Terms Related to Operating Characteristics
| Classifi- cation | Term | Abbre- viation | Unit | Definition |
| Force (torque) | Operating Force (torque) | OF | N, Nm | The force (or torque) that must be applied to the pushbutton to move it from the free position to the operating position. |
| Releasing Force (torque) | RF | N, Nm | The force (or torque) that must be applied to the pushbutton to move it from the operating limit position back to the returned position. | |
| Total Travel Force (torque) | TTF | N, Nm | The force (or toque) on the pushbutton when it reaches the stopper. | |
| Position | Free Position | FP | mm, (°) | The position (or angle) of the pushbutton when there is no external force applied to it. |
| Operating Position | OP | mm, (°) | The position (or angle) of the pushbutton when the movable contact changes from the free position state to the operating position state due to an external force. | |
| Release Position | RP | mm, (°) | The position (or angle) of the pushbutton when the movable contact changes from the operating position state to the free position state due to the reduction of external force. | |
| Total Travel Position | TTP | mm, (°) | The position (or angle) of the pushbutton when it reaches the stopper. | |
| Set Position | SP | mm, (°) | The position of an alternate operation pushbutton when it is in the self-holding state, or the position (or angle) of a selector switch when it is in the self-holding state. | |
| Travel | Pretravel | PT | mm, (°) | The distance (or angle) through which the pushbutton moves in going from the free position to the operating position. |
| Overtravel | OT | mm, (°) | The distance (or angle) through which the pushbutton moves in going from the operating position to the operating limit position. | |
| Movement Differential | MD | mm, (°) | The distance (or angle) through which the pushbutton moves in going from the operating position back to the returned position. | |
| Total Travel | TT | mm, (°) | The distance (or angle) through which the pushbutton moves in going from the free position to the operating limit position. | |
| Releasing Travel | RT | mm, (°) | The distance (or angle) through which the pushbutton moves in going from the returned position to the free position. | |
| Lock Travel Alternate | LTA | mm, (°) | The distance (or angle) through which the pushbutton moves in going from the free position to the set position. |

Terminal Symbols
| Symbol | Meaning |
| COM | Common terminal |
| NC | Normally closed terminal |
| NO | Normally open terminal |
Contact Form
| Name | Contact form |
| Double-throw | 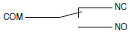 |
| Normally closed | 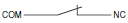 |
| Normally opened |  |
| Double-break | 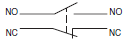 |
Terms Related to IEC60947 and IEC60950
| No. | Term | Explanation | |||
| 1 | Rated operating voltage (Ue) | VAC: 120, 240, 380, 480, 500, 600 VDC: 125, 250, 440, 500, 600 | |||
| 2 | Rated operating current (Ie) | Specified by the manufacturer on consideration of rated operating voltage (Ue), rated frequency, rated energizing time, area of application, and type of enclosure protection. | |||
| 3 | Rated insulation voltage (Ui) | Determined by creepage distance and the dielectric strength. The maximum Ue value must not exceed the maximum Ui value. If there is no Ui value specified, the maximum Ue value is taken as the Ui value. | |||
| 4 | Pollution degree | 1. Either no pollutants are present, or only dried, non-conductive pollutants are present (e.g., clean rooms). 2. Basically, only non-conductive pollutants are present, or only transient conductivity occurs due to condensation (indoor locations, such as offices). 3. Conductive pollutants are present, or non-conductive pollutants are present in locations where condensation is expected (e.g., factories). 4. Conductivity due to impurities is a constant possibility, or conductivity is caused by conductive dust, rain, or snow (e.g., outdoor locations). | |||
| 5 | Electric shock protection class | Class I: These devices require grounding. Electric shock is prevented by basic insulation and charged parts that would be subject to dangerously high voltages if the insulation was damaged, are grounded. Class II: Electric shocks are prevented by double insulation or enforced insulation. Class III: No countermeasures against electric shocks are required because the electric circuits in use operate in a lowenough voltage range. | |||
| 6 | PTI | Proof tracking index. Specified CTI values (comparative tracking indices): Materials satisfying the 175, 250, 300, 375, and 500 levels are denoted as PTI-175, PTI-250, PTI-300, PTI-375, and PTI-500 respectively. | |||
| 7 | IP | IP-(1)(2) (IEC60529) Meaning of first number-Degree of protection against solid materials and people (See below.) Meaning of second number-Degree of protection against water (See below.) | |||
| No. | Meaning of first number | Meaning of second number | |||
| Degree of protection against solid materials | Degree of protection for people | Degree of protection against water | |||
| 0 | No protection | No protection | No protection | ||
| 1 | No penetration by any solid object with a diameter of 50 mm or more. | Cannot be touched with the palm of your hand. | Protects against vertical drops of water. | ||
| 2 | No penetration by any solid object with a diameter of 12.5 mm or more. | Cannot be touch with fingers. | Protects against drops of water approaching at a maximum angle of 15° to the vertical. | ||
| 3 | No penetration by any solid object with a diameter of 2.5 mm or more. | Same as at left. | Protects against sprinkled water. | ||
| 4 | No penetration by any solid object with a diameter of 1.0 mm or more. | Same as at left. | Protects against water spray. | ||
| 5 | Protection against dust | No penetration by any object with a diameter of 1.0 mm or more. | Protects against water jet spray. | ||
| 6 | Dustproof | No penetration by any object with a diameter of 1.0 mm or more. | Protects against high-pressure water jet spray. | ||


