Question
What is a failure rate?
Answer
A failure rate expresses a rough guide to the switchable limits of electronic circuits and other very small loads (i.e., microloads).
The percentage of failures per unit time during continuous relay switching (number of operations) under individually specified test types and loads. The failure rate will change depending on the switching frequency, the environmental conditions, and the expected reliability level. Failure rates must always be checked on equipment under real operating conditions.
The failure rate is listed as the P level (reference value). This expresses the failure level at a reliability level of 60% (λ60) (JIS C5003).
| Level | Failure rate (/operation) |
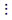 | |
| L | 5 × 10-6 |
| M | 1 × 10-6 |
| N | 0.5 × 10-6 |
| P | 0.1 × 10-6 |
| Q | 0.05 × 10-6 |
 |
Example:
λ60 = 0.1 × 10-6/operation means that 1/10,000,000 failures can be expected at a reliability level of 60%.
Recommended Products
 MY
MY
New Latching Levers for Circuit Checking Added to Our Best-selling MY General-purpose Relays
 LY
LY
Power-switching Compact General-purpose Relays
 G3PE (Three-phase)
G3PE (Three-phase)
Compact, Slim-profile SSRs with Heat Sinks. Solid State Contactors for Three-phase Heaters Reduced Installation Work with DIN Track Mounting.
Other General Purpose Relays FAQ
-
 The Relay does not operate even when voltage is applied. Why is this?
The Relay does not operate even when voltage is applied. Why is this?
-
 We were using G2R General Purpose Relay to turn a solenoid valve ON and OFF, and sparks at the contact damaged the relay after only about 3 months of use. What caused this, and what kind of countermeasure is there for it?
We were using G2R General Purpose Relay to turn a solenoid valve ON and OFF, and sparks at the contact damaged the relay after only about 3 months of use. What caused this, and what kind of countermeasure is there for it?
-
 A Relay burned out. Why is this?
A Relay burned out. Why is this?


